While reading Blade Runner and Neuromancer, we encounter corporations wielding almost unchecked power, often overshadowing governments. Tyrell Corporation’s dominance in Blade Runner and the Tessier-Ashpools’ influence in Neuromancer raise unsettling questions: Are these futures warnings or realities in disguise?
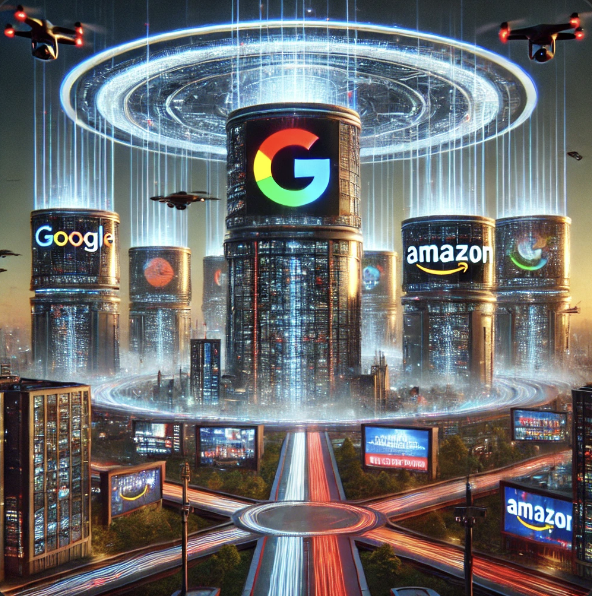
Take the Tyrell Corporation from Blade Runner, which manufactures lifelike “replicants” designed for labor, exploration, and even combat. Tyrell’s massive control over these advanced beings and their fates highlights the ethical dangers of corporate dominance over technology and, by extension, over life itself. In the contemporary world, parallels can be drawn to large tech and biotech companies, some of which have major influence over AI, data privacy, genetic engineering, and more. Companies like Google, Amazon, and Meta shape our digital spaces and impact the physical world in ways that often challenge traditional regulations.
Consider the data privacy issues around social media algorithms or the ethical questions raised by CRISPR and genetic manipulation. These real-world examples, much like the corporations in our cyberpunk narratives, show how the pursuit of profit and influence can lead companies to push ethical boundaries. This raises the question: Are these science fiction worlds a hyperbolic vision of the future or an exaggeration of corporate tendencies we already observe?
For readers interested in exploring this topic further, I’d recommend supplemental readings like recent articles on data privacy concerns from the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) or analyses of corporate ethics in genetic research from Nature. Embedding images of scenes from Blade Runner and Neuromancer could also enhance the post by visually contrasting fiction with present-day corporate logos or data-privacy infographics, bringing readers closer to the eerie overlap between these worlds.
Are we already on the path toward a corporate-dominated dystopia, or do these narratives exaggerate our fears? This discussion is crucial as we navigate a future where corporations play an increasingly central role in both innovation and ethics.